Document Processing is a family of features—like OCR—that adds functionality and automation to scans or improve image quality:
- OCR
- Batch Splitting
- Blank Page Removal
- Despeckle and Deskew
- Document Processing in the cloud or self-hosted
- FAQs
OCR
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is the process of taking an image, such as a scanned document, and reconstructing its text. This allows scanned documents to become searchable and/or editable.
Text-searchable documents have two major benefits over other scan outputs:
- You can search for and copy specific content within the document.
- If the document has been added to a document management system, you can find the document by searching for its content.
Performing OCR is a resource intensive process that can add seconds or tens of seconds per page to the time it takes to deliver a document. For this reason, enable OCR on scan actions where it is most useful, not where fast delivery is more important.
Currently PaperCut MF supports the following text-searchable file types:
- PDF (text-searchable)—PDF v1.4 with PDF/A-1 compliance according to the requirements defined by the PDF/A standard.
- DOCX
Supported languages
OCR supports extracting text for approximately 100 languages. You can choose to use up to 10 of those languages, however for the best performance, limit your choices to a maximum of four languages.
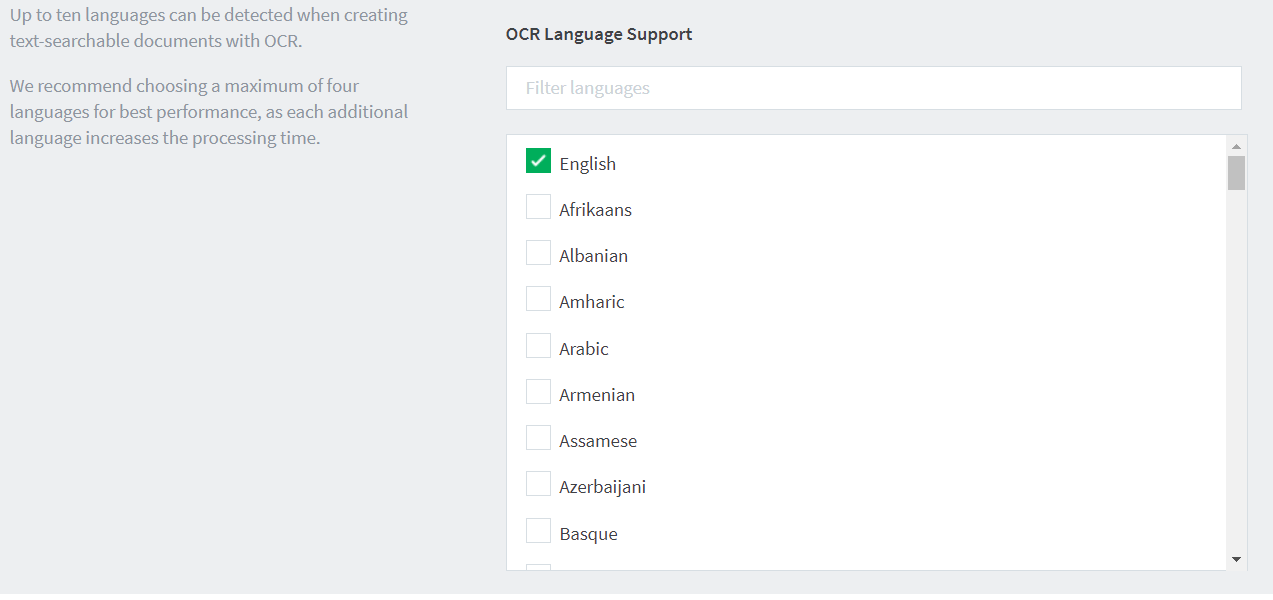
Supported languages
| A | F | L | S |
| Afrikaans | Faroese | Lao | Sanskrit |
| Albanian | Filipino | Latin | Scottish Gaelic |
| Amharic | Finnish | Latvian | Serbian |
| Arabic | Flemish | Letzeburgesch | Sindhi |
| Armenian | Franksh | Lithuanian | Sinhala; Sinhalese |
| Assamese | French | Luxembourgish | Slovak |
| Azerbaijani | G | M | Slovenian |
| B | Gaelic | Macedonian | Spanish |
| Basque | Galician | Malay | Sundanese |
| Belarusian | Georgian | Malayalam | Swahili |
| Bengali | German | Maltese | Swedish |
| Bosnian | Greek | Maldivian | Syriac |
| Breton | Gujarati | Maori | T |
| Bulgarian | H | Marathi | Tagalog |
| Burmese | Haitian | Moldavian | Tajik |
| C | Haitian Creole | Moldovan | Tamil |
| Catalan | Hebrew | Mongolian | Tatar |
| Cebuano | Hindi | N | Telugu |
| Cental Khmer | Hungarian | Nepali | Thai |
| Cherokee | I | Northern Kurdish | Tibetan |
| Chinese - Simplified | Icelandic | Norwegian | Tigrinya |
| Chinese - Traditional | Indonesian | Occitan (post 1500) | Tonga (Tonga Islands) |
| Corsican | Inuktitut | Oriya | Turkish |
| Croatian | Irish | P | U |
| Czech | Italian | Panjabi | Uighur |
| D | J | Pashto Persian | Ukrainian |
| Danish | Japanese | Pilipino | Urdu |
| Dhivehi | Javanese | Polish | Uyghur |
| Divehi | K | Portuguese | Uzbek |
| Dutch | Kannada | Punjabi | V |
| Dzongkha | Kirghiz;Kyrgyz | Pushto | Valencian |
| E | Kazakh | Q | Vietnamese |
| English | Korean | Quechua | W |
| Esperanto | Kurdish | R | Welsh |
| Estonian | Romanian | Western Frisian | |
| Russian | Y | ||
| Yiddish | |||
| Yoruba |
Batch Splitting
Batch Splitting transforms a single large input document into multiple output documents. It’s ideal for use with high-capacity document feeders, and when scanning batches of forms or invoices.
Batch Splitting is applied at the scan action level, and has two options:
- Split every N pages (set by the administrator)
- Split on blank separator pages
When splitting on blank separator pages, a detected blank page becomes the last page of the current document and the following non-blank page becomes the first page of the next document.
Output documents all share the same image and quality settings like DPI, color, and orientation. And they are all delivered to the same destination with the same root file name appended numerically for each document, like this:
- %FileName%_1
- %FileName%_2
- %FileName%_3
You can use splitting on blank pages in combination with Blank Page Removal. The blank pages are first detected to trigger splitting, then removed from the resulting individual documents.
Blank Page Removal
Blank Page Removal detects and removes pages with no content. This helps reduce the size of scanned documents and provides a more seamless experience when reading the digital output.
You configure Blank Page Removal ON or OFF at the scan action level. It defaults to OFF.
It works by analyzing each page against a white space threshold, and deletes pages which meet or exceed the threshold. This threshold is set by default, but you can manually adjust it using the system.scan.docproc.blank-threshold
configuration key
to fine-tune sensitivity.
PaperCut MF applies Blank Page Removal at the page level, not sheet level, so it is ideal for shrinking scans of single-sided content.
When there are multiple blank pages in a row, they are treated as one blank page and are removed together.
Despeckle and Deskew
These settings are applied globally, from the Options > Capture page. When activated, they apply to all new and existing scan actions with no additional setup required.
Despeckle detects pixel noise in the scanned image and removes it. This is useful when scanning documents that have already been copied or printed multiple times, like student forms, or when scanning documents using older imaging hardware.
Deskew detects crooked documents, and straightens them by up to 45 degrees. This type of straightening is most helpful when documents are being scanned individually on the glass, where there’s a high risk of human error or paper shifting alignment as the lid is opened and closed.
Both Deskew and Despeckle help improve the accuracy of OCR, and can be used individually or in combination with any other Document Processing features.
Document Processing in the cloud or self-hosted
PaperCut MF provides the ability to run Document Processing using the PaperCut MF Cloud Document Processing service (formerly MF Cloud OCR Service), (one of PaperCut’s Cloud Services ), or using your own self-hosted infrastructure:
PaperCut Cloud Document Processing service — Let the cloud do all the heavy lifting and benefit from:
improved local infrastructure performance
automatically deployed service updates. Always have the latest performance improvements and functionality.
The PaperCut MF Cloud Document Processing service processes concurrent jobs in parallel and handles any scaling of the service, even when there is a high user load.
Self-hosted Document Processing (On-prem) — For use when there’s a requirement to host Document Processing on your organization’s local infrastructure, and you have a high performing Application Server or resources to configure multiple Document Processing servers.
Some organizations have a requirement for data to stay within their own managed infrastructure or even on their own premises, typically for regulatory or compliance reasons. Be aware that this involves installing the service on selected infrastructure and keeping it updated by installing new versions. For more information, take a look at the Document Processing FAQs , or to get started, see Set up self-hosted Document Processing
FAQs
Is self-hosted Document Processing different to Cloud Document Processing?
As far as the output is concerned, no.
Cloud Document Processing accepts scan data from around the world and processes it in the region chosen by the organization. This means that data might travel outside or be processed outside the country of origin.
Cloud Document Processing scales according to scan job requirements, whereas self-hosted Document Processing requires you to manage local infrastructure and manually install server updates.




Comments